How To Choose Between These 7 Types Of Heating Systems

Top Benefits Of Having A Natural Gas Heating System
October 7, 2022
Common Furnace Problems And How To Fix Them
December 15, 2022Heating systems transfer thermal energy from fuel systems to heat the living spaces in your home. If you’re wondering how to choose between heating systems; there are several types, and each general type has more specific variations. Some HVAC systems provide both heating and cooling, and some work independently.
The purpose of all heating systems, no matter the type, is to use fuel to warm your home. There are various fuel sources a heating system can use; this includes natural gas, propane, fuel oil, biofuel, solar and electricity. Below are some examples of seven different heating systems and information about each. This information can assist you as you decide how to choose heating systems.
1.Forced Air Cooling/Heating Systems
This heating system is the most common in homes in North America. This system delivers warmed air through a network of ducts using a blower fan. These systems can adjust the room temperature quickly since they share the same blower and ductwork as the air conditioning system.
Overall this is an efficient HVAC system. The cost of installing a new forced-air HVAC depends on the square footage of your home, and a larger house will require a unit with more strength, increasing the overall cost. These systems are typically between $5000 and $10,000 and can last up to 25 years.

2. Gravity Air Furnace Systems
Gravity air furnaces also distribute warm air through a network of ducts. However, the air is not forced by a blower; these systems rely on physics. Warm air rises, and cool air falls. These systems are slower at temperature adjustments as they operate using simple convection currents.
These furnaces are often found in older homes. The gravity air furnace is located in the basement, heating the air so that it rises through the ducts into the other rooms of the house. Colder air can be returned to the furnace using a system of cool air return ducts. These systems are no longer installed; they have low maintenance costs and continue to perform effectively in most older homes.
3. In-Floor Radiant Heating Systems
These quiet furnaces involve plastic water tubing installed into concrete slab floors or attached to the bottom or top of wooden floors. These systems heat a little slower and take slightly longer to adjust than forced air heat.
These systems are unique because they heat objects and materials. Instead of heating the air, in-floor radiant heating warms up the furniture and flooring. These systems cost between $1,800 and $6,000. Most whole-home radiant systems use hot water to distribute heat which cannot combine with air conditioning.
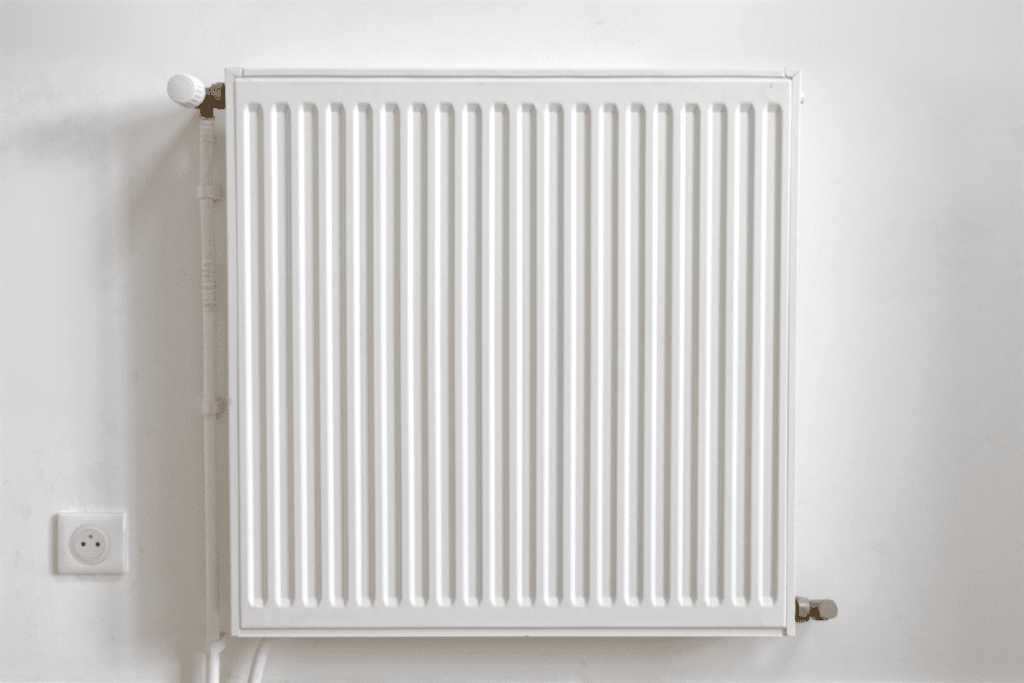
4. Traditional Radiator and Boiler Systems
Traditional radiator and boiler systems use a central boiler that produces steam or hot water. This steam and hot water flow through pipes to radiator units that are located throughout the home. These systems are standard in older homes and apartments in North America.
There are two types of systems that use these old radiators. Older versions circulate steam that condenses back to water after reaching the radiator, and modern radiator systems circulate hot water using electric pumps to reach the radiator. These heating systems cost between $3.700 and $8,200.
5. Hot Water Baseboard Radiator
Hot water baseboard systems are another modern form of radiant heating. This system uses a central boiler that heats water that circulates through the pipes. The water then reaches a baseboard heating unit that uses thin metal fins to radiate the heat from the water into the room. These systems can last several decades and cost between $450 and $1,200.
6. Heat Pump Heating Systems
Heat Pump Heating systems are the newest technology that uses the same concept as air conditioners, extracting heat from the air and circulating it through an indoor air handler. Other systems pull heat from the ground or water, but air-source heat pumps are used in standard homes.
Heat pump systems are energy efficient but are more suitable for milder climates. These systems typically cost about $4,200 to $7,300 and last up to 15 years. Commonly, heat pumps are powered by electricity but there are also natural gas systems available.
7. Electric Resistance Heating
These systems are not typically used in homes due to the high cost of electricity. Electric resistance heating is used in smaller rooms or seasonal rooms. These heaters also warm the objects in a room like radiant electric heaters. Electric heaters are inexpensive to install, costing between $450 and $1,200. These heaters also don’t require other equipment such as ductwork, pumps, or air handlers; they are relatively easy to install.
When deciding how to choose between heating systems, it’s essential to consider what best suits you and your home. It’s beneficial to consider each option’s cost and lifespan and ensure you’re selecting an energy-efficient heater. Living water provides heater furnace installation and repair services. Visit our website to learn more.

